Abstract
Objective: To present the efficacy of a combined topical treatment with antibiotic, antifungal, and corticosteroid in managing perianal intertrigo with secondary fungal infection.
Case Presentation: A 25-year-old female presented with inflammatory skin signs in the perianal region, including itching, erythema, discomfort, and signs of fungal overgrowth. These symptoms appeared following a 9-day course of systemic antibiotic (Amoxiclav) and the use of menstrual pads.
Treatment: The treatment consisted of local cleansing with chamomile tea, drying with gentle compresses, and topical application of a cream containing triamcinolone acetonide, neomycin, and nystatin. The cream was applied twice daily during the first week and once daily during the second week.
Results: Marked clinical improvement was observed within 14 days, with complete resolution of symptoms and no reported side effects.
Conclusion: This case demonstrates that combined topical treatment is an effective alternative for complicated intertrigo and highlights the importance of individualized therapy.
Keywords
Perianal Intertrigo; Secondary Fungal Infection; Topical Combination Therapy; Triamcinolone; Neomycin; Nystatin; Case Report; Skin Inflammation; Antifungal Treatment; Corticosteroids.
Introduction
Intertrigo is a superficial inflammatory skin condition that commonly appears in flexural areas such as the axillae, inguinal folds, inframammary region, and perianal area. Factors such as moisture, friction, and poor ventilation contribute to its development [1,2]. Secondary infections, primarily by Candida spp. and occasionally Staphylococcus aureus, may complicate the condition [3]. Diagnosis is primarily clinical, but complicated cases may require additional testing such as microscopy, culture, and dermoscopy. Prompt recognition and appropriate management are essential to prevent complications.
Pathophysiology and Epidemiology
Intertrigo results from continuous skin-to-skin friction, especially in the presence of moisture. The warm and humid environment in skin folds facilitates epidermal maceration and microbial proliferation. Risk factors include obesity, diabetes mellitus, and poor hygiene [1]. Intertrigo is more common in warm and humid climates and can affect individuals of any age, gender, or ethnicity [2].
Case Report
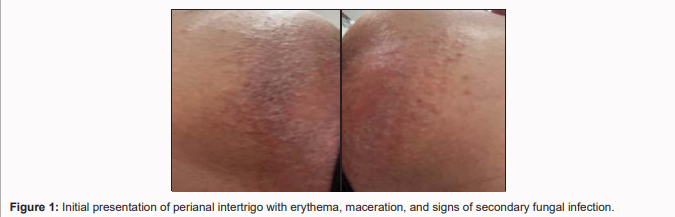
A 25-year-old female presented with erythema, pruritus, discomfort, and local irritation in the
perianal region, which developed during the last two days of a 9-day course of Amoxiclav. The patient
had also been using menstrual pads due to her menstrual cycle. The clinical diagnosis was intertrigo
with secondary fungal infection, based on visual examination and reported symptoms.
Treatment protocol:
- Local cleansing with chamomile tea.
- Drying with gentle compresses.
- Topical cream application containing:
- Triamcinolone acetonide (anti-inflammatory corticosteroid)
- Neomycin (broad-spectrum antibiotic)
- Nystatin (antifungal active against Candida spp.)
Dosing: Twice daily in the first week, once daily in the second week.


Results
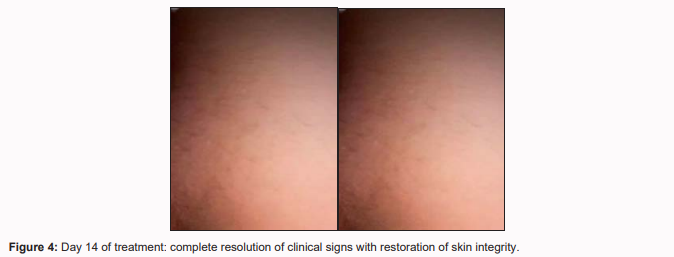
After 7 days, a noticeable reduction in erythema and pruritus was observed. After 14 days, the patient reported
complete symptom resolution with no adverse effects.
Discussion
The management of complicated intertrigo presents clinical challenges, particularly when associated with
microbial infections. Combined topical therapy with anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and antifungal components
can address the full pathogenesis of the condition and facilitate rapid healing. Triamcinolone reduces inflammation,
while neomycin and nystatin target bacterial and fungal infections, respectively. This case underscores the value of
an integrated approach in managing intertrigo and supports the use of combination creams as a first-line treatment,
in conjunction with hygiene measures and avoidance of irritants [3].
Conclusion
This case report demonstrates the efficacy of combined topical treatment with triamcinolone, neomycin, and
nystatin in managing perianal intertrigo with secondary infection. Complete clinical improvement within two
weeks and absence of side effects suggest that this regimen is a safe and effective option. Emphasis should also be placed on individualized therapy tailored to the underlying etiology.
References
-
1.
Janniger CK, Schwartz RA. Intertrigo and common secondary skin infections. Am Fam Physician. 2005.
-
2.
Leman JA, Holden CA. Intertrigo. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2002.
-
3.
Gupta AK, Bluhm R. Topical antifungal agents for the treatment of tinea infections. Drugs. 2004.







